Did you know up to 38% of women face thinning hair? It’s crucial to spot the early signs. Female pattern hair loss is common. Spotting the signs early makes treatments more effective.
Some may not notice their hair or scalp changing. But signs like a wider part or seeing more scalp can warn of hair loss. Also, finding a lot of hair on your brush or pillow is a clue. We’ll dive into these signs and give tips on checking hair health.
Experts like Dr. Anna H. Chacon from the American Academy of Dermatology offer valuable insights. With advice from the Mayo Clinic too, you’ll learn to spot thinning hair. We’ll explain how this can impact your look and confidence.
Key Takeaways
- Up to 38% of women experience hair thinning, making it a widespread concern.
- Early detection of thinning hair allows for more effective treatment options.
- Common signs of hair thinning include widened parts and increased hair loss in brushes and drains.
- Monitoring hair density changes can help identify early signs of hair loss.
- Healthy lifestyle choices play a crucial role in preventing further hair thinning.
- Comparing photographs can provide visual evidence of hair thinning progression.
The Basics of Hair Thinning
It’s essential to understand hair thinning if you care about hair health. When our bodies don’t replace hair as fast as we lose it, thinning occurs. This leads to less hair on our heads.
Hereditary factors like male-pattern and female-pattern baldness play a big role. Men may see baldness start at the crown and spread. Women’s baldness usually begins at the scalp’s center.
Hair loss can happen for many reasons, including hormone changes, medical issues, and getting older. Stress can also cause a condition called telogen effluvium, which leads to more hair falling out. Normally, people lose 50 to 100 hairs a day. Losing more could mean your hair is thinning.
Genetics isn’t the only cause of thinning. Hairstyles that pull tight can damage hair, leading to traction alopecia. To prevent more hair loss, look at your habits and diet. You might need special hair products or supplements. For more tips, check this source.
| Hair Loss Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Hereditary Hair Loss | Common in both men and women, often evident by the age of 30. |
| Telogen Effluvium | Triggered by stress, leading to diffuse thinning across the scalp. |
| Traction Alopecia | Resulting from tight hairstyles, leading to hair loss around the hairline. |
| Normal Shedding | 50 to 100 hairs lost daily is considered normal. |
| Excessive Shedding | More than 100 hairs daily may indicate underlying issues. |
Common Hair Loss Symptoms
Understanding hair loss starts by knowing the difference between normal and worrying signs. It’s normal to lose 50 to 100 hairs daily. But, if you’re losing more, it could signal a problem. Excessive hair fall can lead to thin patches, which might mean there’s a deeper issue at play.
Understanding Shedding vs. Hair Loss
We all shed some hair every day, which is part of how hair grows. But if you start seeing noticeable bald spots or thinning, it could be too much shedding. Things like genetics, stress, and health problems can cause hair to fall out more than usual. For example, alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease that leads to patchy hair loss. Sometimes, you might even find more hair on your pillow or in your hairbrush.
Recognizing the Difference Between Temporary and Permanent Hair Loss
It’s important to know if hair loss is temporary or permanent to find the right solution. Temporary hair loss might come from life changes, being sick, or not getting enough of certain nutrients. Hair usually grows back once these issues are fixed. On the other hand, permanent hair loss, like androgenetic alopecia, is often genetic and affects both men and women. Early detection makes managing and treating hair loss easier.
How to Tell If Your Hair Is Thinning
Knowing the signs of thinning hair early can help a lot. If you notice changes in how thick your hair feels, its texture, or your hairline, these could be signs. Looking at the condition of your scalp and how your hair looks can be very telling.
Using Mirrors to Assess Your Hair and Scalp
Use mirrors from different angles to check your scalp and hairline. With a hand mirror and a wall mirror, you can easily see the back and sides of your head. This lets you spot signs of thinning early.
Check your scalp regularly to catch any changes right away.
Taking Comparison Selfies for a Visual Reference
Taking selfies from different angles over time is a good way to track changes. By comparing these pictures to older ones, you can see if your hair is getting thinner. This method makes it easier to understand thinning hair.
Signs of Receding Hairlines
A receding hairline is a clear sign of hair thinning, especially in men. It usually starts at the temples or crown and gets worse without timely action. In women, a widening part line shows up, demonstrating different patterns of hair loss.
Many things can lead to a receding hairline and bald spots. Genetics is a big factor, as conditions like androgenic alopecia affect both genders. Stress, changes in hormones, and certain treatments can make hair loss worse. Importantly, frontal fibrosing alopecia mainly hits postmenopausal women in the forehead region.
Knowing how a receding hairline progresses is key for early help. In men, it often begins with slight recession, followed by more hair loss and visible bald patches. By 50, a shocking 85% of men see hair loss from androgenetic alopecia. Being aware early on is important.
Treatments like finasteride, topical minoxidil, and hair transplant surgeries can help. Newer options like platelet-rich plasma therapy and light therapy look promising for hair growth. Using gentle hair care and avoiding tight hairstyles are good home strategies for those with a receding hairline.
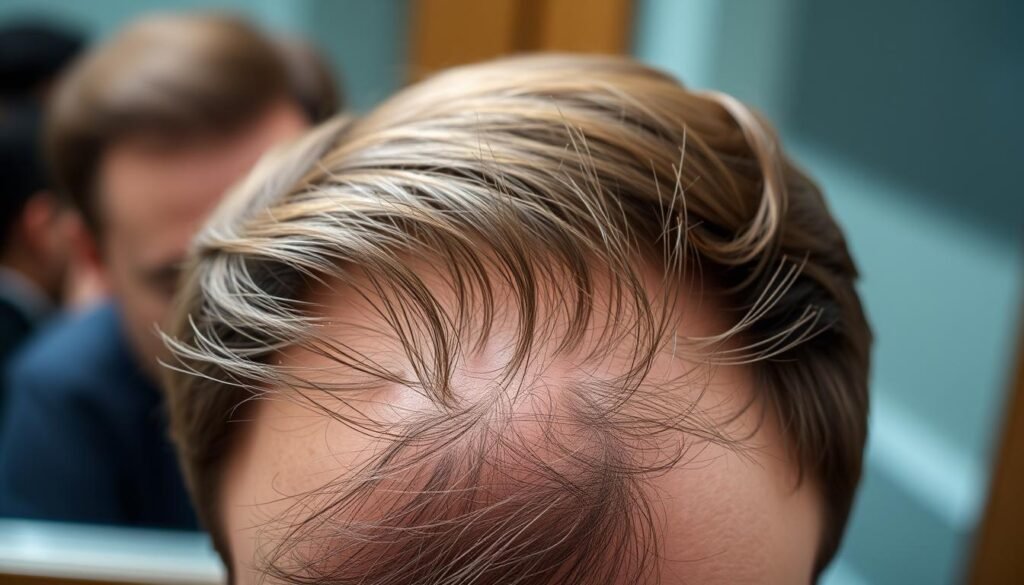

Excessive Shedding Indicators
Keeping an eye on your hair loss is key to healthy hair. It’s good to check for too much shedding. This helps catch problems early for quick action.
Monitoring Hair Loss During Showering and Styling
When you shower, pay attention to the hair that falls out. Usually, losing 50-100 hairs daily is normal. Seeing hair fall out while you shampoo or condition gives useful clues.
Hair loss during styling is another sign. If you see more hair in the drain, on your comb, or brush, it’s time to look into your hair health.
Identifying Common Areas for Shed Hair Accumulation
Shed hair tends to gather in certain places like the bathroom floor, pillows, or clothes. Spotting these can help you figure out if you’re losing too much hair. A big increase in hair at these spots, more than usual, means you should check it out.
Things like stress or hormones can cause lots of shedding. Talking to a hair loss expert can help. They can tell you if your shedding is normal or something more serious. For more info on hair loss symptoms, check out this resource.
| Hair Length | Mean Shedding Score (No FPHL) | Mean Shedding Score (With FPHL) |
|---|---|---|
| Short | 2.5 | 7.25 |
| Medium | 2.35 | 7.0 |
| Long | 2.4 | 7.14 |
Knowing the difference in shedding between women with and without FPHL is crucial. It helps spot excessive shedding early. That way, you can address the root cause quickly.
Identifying Hair Density Reduction
Hair density reduction changes how we look and feel about ourselves. People might not quickly notice when their hair starts to thin. But some signs, like a lighter ponytail or smaller bun, can show it’s happening. Humans usually have between 80,000 to 120,000 hairs on their heads. When this number drops, it might worry us about our hair’s health.
To check hair density, we group it as low, medium, or high. Hair with low density often shows more scalp and has a ponytail circumference of less than two inches. Medium-density hair looks balanced and it’s a bit harder to see the scalp. High-density hair means the scalp is hard to see, with a ponytail that’s more than four inches around. Knowing these groups helps us care for our hair better. It affects our choice of products and how we style our hair.
Many things influence hair density, including genetics, diet, and overall health. Changes in hormones or chronic illnesses can thin out our hair. Paying attention to these signs is important. It can lead us to look after our health and hair care better. For more on hair density, check out this helpful resource.
| Density Category | Ponytail Circumference | Scalp Visibility |
|---|---|---|
| Low Density | Less than 2 inches | Scalp easily visible |
| Medium Density | 2 to 3 inches | Scalp somewhat visible |
| High Density | 4 inches or more | Scalp difficult to see |
Balding Patches: What to Look For
Balding patches are clear signs of hair loss that worry many people. They can show up on any part of the scalp. The size and shape of these patches can be very different. In alopecia areata, one might lose hair suddenly in spots. Others may see bigger areas getting thin, which points to male or female pattern baldness.
Noticing balding patches early is key to dealing with them. Usually, the first sign is a round or oval smooth spot without hair. This condition’s nature is unpredictable. Some might see hair come back in one place but lose it in another. It’s important to keep an eye on these changes and talk to a doctor about them.
Balding does not only affect scalp hair. Eyebrows and eyelashes can also get sparse. Those with alopecia universalis might lose all body hair. This can also make nails weak and break easily. Knowing these signs helps in finding the right treatment. For more on how to treat balding patches, check this comprehensive article.
Increased Scalp Visibility
Seeing more of your scalp can be the first clue that your hair might be thinning. Looking at how your hair lays can reveal signs of thinning that need attention. This can be due to aging or even how we style our hair. Spotting these hints early helps us act quickly to manage the issue.
Recognizing More Skin Through Your Hair
Noticing more skin when you look at your hair could mean it’s getting thinner. As the amount of hair decreases, the scalp starts to show more. This is more visible when hair is pulled back tightly, like in ponytails or braids. People with fine hair might see their scalp more because there’s more space between hairs.
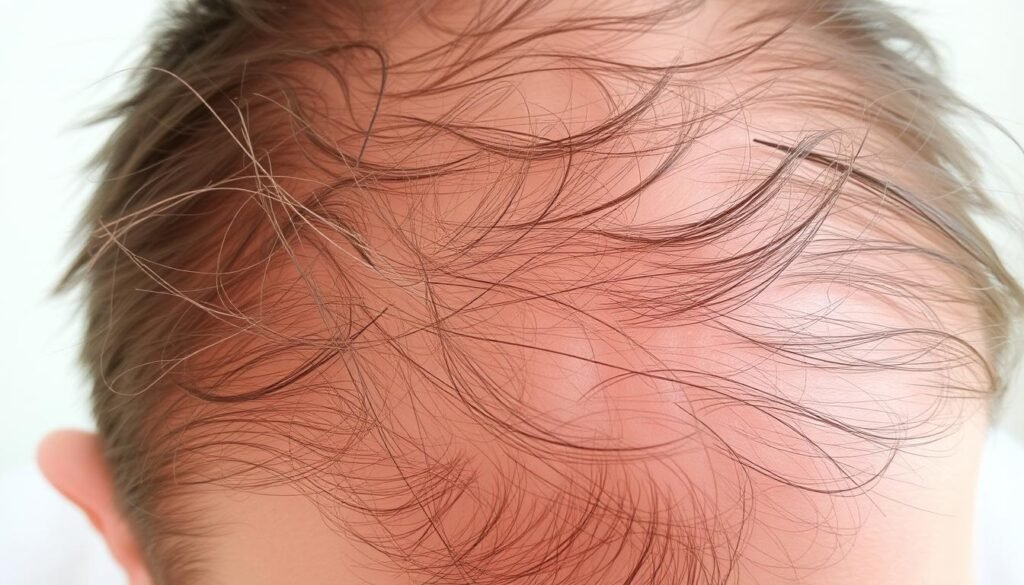
As we get older, our hair tends to thin out, making the scalp easier to see. Shifts in hormones can also lead to hair changes, pointing to deeper issues. Eating habits and stress can make thinning more noticeable. This shows how our lifestyle affects our hair’s health.
| Factor | Impact on Scalp Visibility |
|---|---|
| Hair Density | Lower density leads to more visible scalp. |
| Hair Thickness | Thinner strands cause increased visibility compared to thicker strands. |
| Aging | Natural thinning increases scalp visibility. |
| Hairstyles | Tight styles emphasize scalp exposure. |
| Environmental Factors | Stress and diet impact overall hair density. |
It’s important to keep an eye on how much of your scalp you can see. Checking this regularly and talking to hair care experts can help. They can offer ways to keep hair looking full and healthy.
The Impact of Hairstyles on Hair Thinning
Certain hairstyles can really affect how healthy our hair is. Styles that pull tightly, like ponytails and braids, can harm hair roots. If we wear these styles a lot, it might lead to thinning hair.
Signs that our hairstyle is causing trouble include a receding hairline and seeing more of our scalp. Other red flags are scalp pain and more hair falling out than usual.
- Receding hairline
- Thinning along the crown
- Visible scalp
- Pain or discomfort in the scalp
- Breakage and split ends
- Increased hair shedding
Hairstyles that are heavy or pull on your hair, like dreadlocks, can be bad for hair follicles. Studies say our hair is thickest at 27, then starts to thin in our mid-30s. This can be harder for women, who might face more hair thinning.
But, don’t worry, there are treatments for hair loss due to hairstyles. These help a lot.
- Scalp massages to enhance blood circulation
- Moisturizing hair masks for increased hydration
- Adopting loose hairstyles to minimize tension
- Utilizing heat protectants to safeguard against damage from styling tools
Understanding how hairstyles impact hair thinning helps us make better choices. By changing how we style our hair, we can protect it better.
| Hairstyle | Impact on Hair Health |
|---|---|
| Tight Ponytails | May lead to traction alopecia due to constant tension |
| Box Braids | Can strain roots and weaken hair |
| Long Dreadlocks | Risk of traction on follicles, resulting in hair thinning |
| Wet Updos | Increased tension on wet hair can cause breakage |
| Pin-Straight Styles | Frequent use of heat can damage hair strands |
Role of Emotional and Physical Stressors
Emotional stress and physical stress can harm our hair, leading to thinning. Studies show stress is linked to hair loss. For example, chronic stress raises corticosterone, slowing hair growth in mice studies.
Mice without adrenal glands showed quick hair regrowth. This points to stress hormones playing a role in hair loss. Mice immune to corticosterone showed no slowdown in hair growth, hinting at hormones affecting stem cells.

Using GAS6 on these mice reversed the effects of high corticosterone. This could help us treat hair loss due to stress. Normally, people lose 50 to 100 hairs a day. Under severe stress, this can jump to 70%.
Stress-related hair loss gets noticeable 3 to 6 months after the stress starts. Telogen effluvium can spread this loss all over rather than in patches. Long-term stress might permanently damage hair follicles, making recovery slower.
Women often see less hair volume, especially on their head’s top, due to emotional stress. Losing more than 100 strands a day can signal stress impact. Though usually temporary, stress-induced hair loss can require treatments like Minoxidil and Finasteride.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
Seeing a healthcare provider for hair loss is very important. Immediate consultation is crucial when noticeable signs of hair thinning arise. Professionals possess the expertise to conduct thorough assessments and recommend appropriate treatments tailored to individual cases.
Various health factors contribute to hair loss, including genetics, hormonal changes, and nutritional deficiencies. A healthcare provider can perform essential blood tests to identify any deficiencies or underlying medical conditions, thus guiding effective treatments. For instance, conditions like autoimmune diseases or thyroid dysfunction can manifest through hair thinning and require specific medical interventions.
Dermatologists highlight the benefits of early intervention in addressing hair loss concerns. Treatment options may include corticosteroid injections, minoxidil, and advanced therapies like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) or laser therapy. Each of these alternatives can have distinct effectiveness based on the cause of hair thinning.
Self-treatment may sometimes make things worse. A healthcare provider can ensure that individuals receive a comprehensive evaluation and practical guidance. This proactive approach helps preserve hair quality and overall scalp health. Individuals experiencing issues such as unexplained hair loss patterns or significant thinning should not hesitate to seek professional advice for optimal outcomes.
Conclusion
It’s important to know if your hair is getting thinner. Look for signs like more scalp showing, more hair falling out, and a hairline that’s moving back. Finding out early can really help, because you can start doing things to make it better sooner.
Why does hair get thinner? It could be because of your genes, changes in hormones, or how you live your life. Knowing this can help you understand what to do. Treatments like using a special laser cap, taking medicine, or trying other products can help. For some, surgery might be the right choice to look into.
If you watch your hair closely and know what to look for, you can take action early. This means you can find the best ways to keep your hair looking the way you want. Paying attention to the signs we talked about can help you keep your hair healthy and keep you feeling good about how you look.