Surprisingly, 85% of men face some degree of hair loss by the age of 50. This issue affects both men and women and can start in the teen years. Noticing the early signs is key. Quick action might lead to effective treatments and even hair regrowth. Spotting signs like thinner hair or a receding hairline is important. It helps identify thinning and deals with the emotional side of hair loss.
Hair loss comes from many causes like genetics, hormone changes, or health problems. This article will help you spot early signs of balding, understand different types of hair loss, and highlight why early detection matters. To learn about specific signs, check out this guide on spotting hair loss.
Key Takeaways
- Hair loss can begin early, impacting both genders and often starting in the teenage years.
- The average person loses between 50 to 100 hairs daily, so increased shedding may signal concern.
- Recognizing early signs of balding can facilitate timely treatment and prevention strategies.
- Genetics, hormonal shifts, and various medical conditions significantly contribute to hair loss.
- Emotional impact is common with hair loss, making awareness and understanding vital.
Understanding Hair Loss and Its Types
Hair loss can affect anyone, no matter their gender or age. It’s vital to know the different kinds of hair loss to manage and treat them well. The most common type is androgenetic alopecia, which includes male and female pattern baldness.
Male pattern baldness may start in puberty and get worse slowly, over years. It usually begins with thinning hair at the temples and crown. Female pattern baldness, however, typically starts with subtle thinning in the 40s or later. It seldom leads to complete baldness.
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease that causes sudden bald spots. It can happen to both adults and kids. Luckily, about 90% of people with this condition see their hair grow back in a few years.
Telogen effluvium is a temporary hair loss from stress, sickness, or hormonal changes. Cicatricial alopecia, a rare type, causes permanent loss as scar tissue replaces hair follicles.
- Tinea capitis: A fungal infection leading to hair loss in children, treated effectively with antifungal medications.
- Centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: This type is most common in Black women, often presenting as a small bald patch in the center of the scalp.
- Hair shaft abnormalities: These issues weaken strands, resulting in breakage and subsequent hair loss.
An average adult’s head has about 100,000 to 150,000 hairs. They lose up to 100 of these each day. Knowing about different hair loss patterns helps people find the right solutions for their conditions.
| Type of Hair Loss | Causes | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Androgenetic Alopecia | Genetics, Hormonal changes | Gradual thinning, male/female patterns |
| Alopecia Areata | Autoimmune Response | Sudden patchy hair loss |
| Telogen Effluvium | Stress, Illness, Hormonal changes | Temporary thinning of hair |
| Cicatricial Alopecia | Scarring of hair follicles | Permanent hair loss |
| Tinea Capitis | Fungal Infection | Localized hair loss in children |
Recognizing different hair loss types helps in getting timely help and effective treatments.
The Impact of Genetics on Hair Loss
Genes play a big role in hair loss. Many people who lose hair have family members with the same issue. About 80% of men face male-pattern baldness by 80 years old. Nearly half of all women deal with similar issues by the same age. Knowing your family history of baldness is key.
Research shows genes cause about 80% of male-pattern baldness. A study found men with a specific gene are twice as likely to lose hair. This shows hair loss runs in families across generations.
A lot of people losing their hair had fathers with the same problem. This points to hair loss being passed down. While other factors play a role, genes are the main cause.
Living healthy can help those worried about losing hair. Eating right, sleeping well, and exercising can improve hair health. Adding treatments like minoxidil or finasteride can also help.
| Factor | Statistical Insight |
|---|---|
| Men with MPB by Age 80 | 80% |
| Women with Hair Loss by Age 80 | 50% |
| Genetics Account for MPB | 80% |
| Risk with Baldness Gene | Twice the risk |
| Familial Connection | 80% of those bald had a father with similar loss |
Learn more about hair loss by reading this detailed guide. Knowing about genetics helps people make better choices for their hair care and loss treatment.
Common Causes of Hair Loss
Many factors can cause hair loss in both men and women. The most common is hereditary hair loss, leading to thinning and bald patches. Hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause also play a big role. Conditions like PCOS show how hormones can affect your hair.
Stress can make your hair fall out too. This can happen after injuries, surgeries, or big changes in life. Thankfully, hair usually grows back once you’re less stressed.
Eating poorly can make hair loss worse. If you’re low on iron, zinc, or biotin, your hair might suffer. Bad hair care, like overusing chemicals or tight hairstyles, can also damage hair roots. This can lead to traction alopecia, which is permanent hair loss.
A healthy scalp is important for hair growth. Issues like infections or psoriasis can cause a lot of hair to fall out. But with the right treatment, hair can often grow back. Sometimes, changing your lifestyle isn’t enough. That’s when treatments like hair restoration could help.
Medicines might also make your hair fall out. But this usually stops when you no longer take the drug. Knowing the different reasons for hair loss helps you choose the best way to treat it.
| Cause | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Hereditary | Common male and female pattern baldness. | Genetic |
| Nutritional Deficiencies | Lack of vitamins/minerals like iron and biotin. | Dietary |
| Hormonal Imbalances | PCOS and menopause affecting hair growth. | Physiological |
| Stress-related Hair Loss | Shedding due to emotional or physical stress. | Psychological |
| Infections | Conditions like psoriasis causing shedding. | Medical |
| Chemotherapy | Rapid hair loss due to cancer treatment. | Treatment-related |
| Traction Alopecia | Permanent hair loss from tight hairstyles. | Hair Care |
Early Signs of Balding
Finding the early signs of balding is key to combatting hair loss. There are a few tell-tale signs that your hair might be thinning. Knowing these can help you act fast and possibly stop it from getting worse.
Thinning Hair at the Temples
Thinning hair at the temples is often one of the first signals. This area may show more scalp, creating an “M” shape. This shape is common in men with a receding hairline. Spotting this early can help in taking action before hair loss progresses.
Receding Hairline Patterns
A receding hairline is another big clue. It changes how the forehead looks and can be pretty noticeable. Watching for these changes helps catch early androgenetic alopecia. It happens in both men and women.
Hair Thinning on the Crown
Hair getting thinner on the crown is a warning of early hair loss. As the hair thins out, the scalp becomes more visible. Spotting this helps assess the severity of hair loss and may hint at future bald spots.
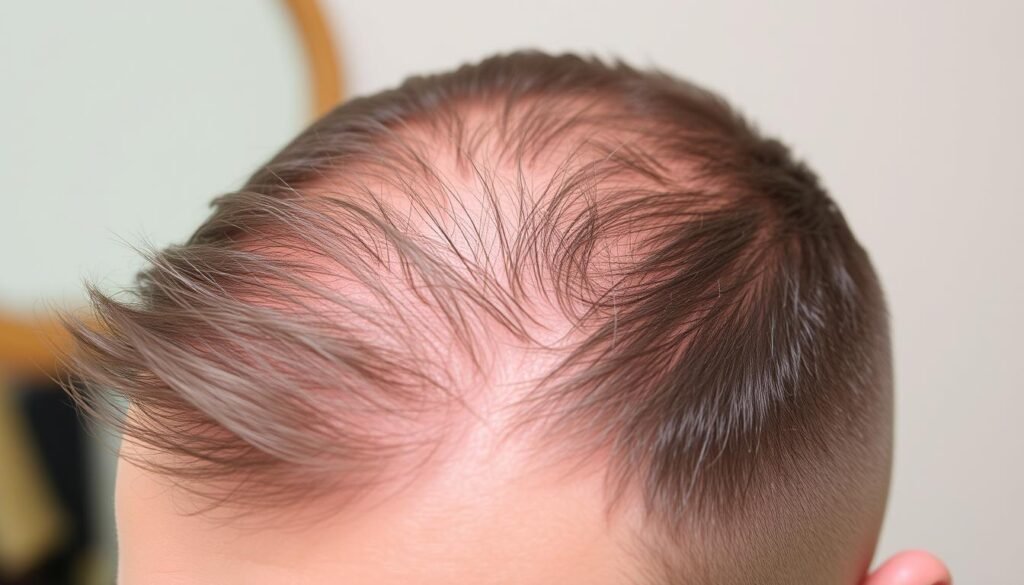
| Indicator | Description | Potential Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Thinning Hair at the Temples | Hair begins to thin noticeably at the temple area. | Formation of an “M” shaped hairline. |
| Receding Hairline Patterns | The hairline gradually moves back from the forehead. | Increased visibility of the forehead; signs of androgenetic alopecia. |
| Hair Thinning on the Crown | Hair becomes finer and more sparse at the crown. | Development of bald spots over time. |
Noticing these signs early lets people take charge. It lets them find the right help, slowing or managing their hair loss effectively.
Identifying Other Types of Hair Loss
Besides the usual balding, some people face sudden hair loss. Alopecia areata and telogen effluvium are two types. They have unique signs and challenges.
Alopecia Areata: Sudden Bald Spots
Alopecia areata leads to unexpected bald patches. This condition attacks hair follicles directly. It creates visible bald spots quickly, without thinning first.
For many, these bald spots are worrying. But knowing about alopecia areata helps in managing its impact.
Telogen Effluvium: Shedding After Stress
Telogen effluvium results from stress, causing more hair to shed than usual. It happens after big life changes or stress. People with this condition should understand the stress-hair loss link. This knowledge helps them seek the right help.
How Age Affects Hair Loss Patterns
As people age, they may face different stages of hair loss. It’s often linked to age, gender, and genetics. Aging leads to changes in the body that affect hair growth.
For men, hair thinning starts in their 20s and gets worse by 30. By 35, 66% of men have noticeable hair loss. By 50, 85% see a big change in hair thickness. By 60, around two-thirds face balding, which mostly means hair receding from the temples and thinning at the crown.
Women also deal with hair loss. About 25% experience it, especially from a condition called androgenetic alopecia. Unlike men, women see these changes later, but by 70, nearly 40% have thinner hair. They might notice thinning at the top of their head or more scalp showing.
Menopause and hormonal changes can make hair loss worse for women. Their hair might get finer and weaker. Seeing a dermatologist can help you understand hair loss and find the right treatment. Early recognition is key for both men and women to take care of their hair. The aging process affects everyone, but knowing the signs can help manage hair health better.
Recognizing Non-Hair Loss Symptoms
Knowing how symptoms differ is key, especially with hair loss worries. Issues like an itchy scalp, dandruff, and dry ends aren’t always about losing hair. Understanding these symptoms unrelated to hair loss can reduce stress.
An itchy scalp might be due to allergies, using too many products, or conditions like seborrheic dermatitis. Dandruff usually means a flaky scalp, not losing hair. These signs don’t always predict baldness.
Let’s separate hair issues from other symptoms with this table:
| Symptom | Potential Cause | Relation to Hair Loss |
|---|---|---|
| Itchy Scalp | Allergic reactions, dry skin | Unrelated |
| Dandruff | Dry skin, fungal infections | Unrelated |
| Hair Thinning | Genetics, medical conditions | Related |
| Patchy Loss | Alopecia areata | Related |
Seeing symptoms like an itchy scalp or dandruff as separate from hair loss is smart. If unsure, always check with a specialist. For more on balding signs, visit Dr. Malay Mehta’s guide at this source.
Scientific Tests to Diagnose Hair Loss
Getting the right hair loss diagnosis is key for finding good treatments. Doctors use many tests to find out why someone is losing hair. These tests can spot the exact reasons why hair is getting thinner.
Scalp Biopsy for Follicle Health
A scalp biopsy means taking a tiny bit of skin from your head to check the health of hair follicles. This can show if infections, scars, or other problems are causing hair loss. Doctors can then figure out the best way to treat it.
Trichoscopy for Detailed Analysis
Trichoscopy is a way to look at the scalp and hair up close without surgery. It uses a special microscope. This helps doctors see the health of your hair and scalp clearly. It can lead to the right treatment by showing what’s wrong.
Blood Tests to Identify Underlying Causes
Blood tests can find health issues that might make hair thin or fall out. These tests look at hormones, if you lack vitamins, and other things that could affect your hair. Knowing these can help doctors decide the best way to help you.
Hair Loss Prevention Strategies
Knowing how to prevent hair loss can really make a difference. If you want to keep your hair thick, certain lifestyle changes are key. This includes making small adjustments to what you do each day and what you eat.
What you eat plays a big role in stopping hair loss. Foods full of vitamins and minerals like iron, zinc, and omega-3s feed your hair roots. Adding things like leafy greens, nuts, fish, and lots of fruits to your diet helps keep your hair healthy. You should avoid processed foods with too much sugar and fat because they can harm hair growth.
It’s also important to not be harsh on your hair. Stay away from too much heat from styling tools and harsh chemicals that make hair weak. Choose to air-dry your hair and use natural products instead.
Pulling your hair back too tightly can cause a type of hair loss called traction alopecia. Choose styles that don’t pull your hair to avoid this. Protective styles, when done right, can also protect your hair from the sun and the environment.
Dealing with stress is just as important. Stress can make hair thin and make hair loss worse. Using relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation can really help your mental and hair health.
Scalp massages are a simple way to get the blood flowing to your hair roots. This helps nutrients get to your hair better and leads to healthy hair growth.
| Activity | Benefits for Hair Health |
|---|---|
| Healthy Diet | Provides essential nutrients that strengthen hair follicles. |
| Gentle Hair Styling | Reduces risk of traction alopecia and damage. |
| Scalp Massages | Enhances blood circulation, promoting hair growth. |
| Stress Management | Minimizes hair thinning caused by stress. |
| Avoiding Heat and Chemicals | Protects hair from damage and maintains health. |
Hair Regrowth Treatments: Options Available
Many people facing hair loss find hope in different treatments. It’s key to know what’s out there, from store-bought options to prescriptions. We’ll look into treatments like minoxidil and DHT blockers, and prescription solutions for certain hair loss types.
Minoxidil and Other DHT Blockers
Minoxidil, also known as Rogaine®, is a top choice without needing a prescription. It’s approved by the FDA for pattern baldness. By stimulating hair follicles, it encourages hair to grow back. Though it might cause some initial shedding, positive changes usually happen between four months to a year.
DHT blockers are pivotal in the fight against hair loss. They stop dihydrotestosterone (DHT) from causing hair to thin. Using them with minoxidil can greatly boost your chances of getting your hair back. People often see their hair become thicker and fuller with this combination.
Prescription Medications for Hair Regrowth
For men, finasteride (Propecia®) specifically targets male pattern baldness and is FDA approved. It works by stopping DHT formation. Although it might take a few months to work, many have seen remarkable improvements with regular use.
Women experiencing hair loss have options like antiandrogens and spironolactone. These can slow down hair loss and even reverse it. For those with autoimmune hair loss, corticosteroids are a choice. They start to show results within months, offering hope and a confidence boost.

When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Seeing too much hair fall out can be worrying. It makes you wonder if you should see a doctor about it. Knowing the signs to see a healthcare professional is key for acting fast. If your hair is suddenly falling out, coming out in chunks, or if your scalp itches or hurts, it’s time to get help.
Being quick to act matters, as it can lead to better results from treatment. Hair loss might mean there is a health issue. A doctor can do tests like blood work or scalp checks to find the cause of the hair loss.
Think about if hormone changes, medicines, or stress could be affecting your hair. Talking to a doctor about hair loss lets you explore ways to help and grow your hair back.
| Sign | Action |
|---|---|
| Sudden hair loss | Consult a healthcare professional immediately |
| Hair loss in clumps | Schedule an appointment for evaluation |
| Itchy or painful scalp | Seek medical attention to rule out conditions |
| Changes in hair texture or thickness | Discuss with a doctor for potential underlying issues |
| Accompanying symptoms (e.g., fever or rash) | Contact a healthcare provider urgently |
Knowing when to see a doctor for hair loss is important. It increases the chance of successful treatment and helps you feel confident again.
Conclusion
Hair loss affects millions around the globe. Early detection is key to dealing with this issue. By knowing the early signs, like thinning at the temples and more hair shedding, people can act fast.
Effective hair loss treatment includes both medical help and changes in lifestyle. Those experiencing hair loss should see a specialist. Options range from minoxidil treatment to improving stress management and diet.
Staying alert to changes in hair density is vital. It helps in managing hair loss and boosts well-being. Early action can lead to better chances of hair regrowth, boosting confidence.